GSiMO Columbia University
To simulate gastric cancer (GC) incidence and mortality trends in alignment with SEER data, providing a robust framework for evaluating the cost-effectiveness of various GC screening and prevention strategies. By capturing the natural history of GC and incorporating key risk factors, GSiMo helps assess the potential impact of interventions such as H. pylori test-and-treat, smoking cessation, and endoscopic surveillance.
Contact: Chin Hur ch447@cumc.columbia.edu
Summary
The Gastric Cancer Simulation Model (GSiMo) is a state-transition microsimulation model that simulates the natural history of gastric cancer (GC) in the U.S. population. GSiMo models GC onset, progression, detection, and mortality, incorporating risk factors such as Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection status and demographic variations in risk by race and ethnicity. Developed to inform prevention and treatment strategies, GSiMo aims to identify optimal approaches to reduce GC incidence and mortality, with a particular focus on addressing disparities in outcomes across diverse subgroups.
GSiMo simulates a population of individuals starting from age 18 to 100 for each demographic subgroup: Non-Hispanic (NH) Black females, NH Black males, NH White females, and NH White males. A proportion of the population is initialized as HP-positive and the remainder is initialized as healthy, aligning with estimated HP infection prevalence. Each month, individuals may transition to one of the following non-overlapping health states: healthy, HP infection, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, undetected gastric cancer (Stages I-IV), detected gastric cancer (Stages I-IV), cancer death, and other death.
GSiMo derives fixed parameters from common model input generators including the HP Infection generator and Life Table generator, as well as survival data from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database. For unobservable states (gray boxes in Figure 1) including progression through the Correa Cascade, progression through preclinical cancer, and detection of cancer, parameters are calibrated via a constrained simulated annealing process to SEER GC incidence data and precursor prevalence targets from literature.
Primary outputs from GSiMo include GC incidence and mortality. Secondary outputs include prevalence of precursor lesions, dwell time, and progression rates. Once the screening and intervention component is fully implemented, outputs such as cancer cases and deaths averted, life years gained, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained, and total costs will be added.
Structure of GSiMo
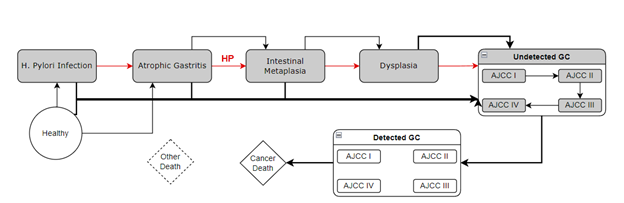
Figure 1: Structure of GSiMo with health states and transition rates.
Bladder models
- Kystis (Brown) Brown
- COBRAS (Ottawa) Ottawa
- SCOUT (NYU) NYU
Bladder Model Comparison Grid (PDF, 145 KB)
See all Comparison Grids & Profiles (Includes historical versions)
Lung models
- BCCRI-LunCan (BCCRI)
- BCCRI-Smoking (BCCRI)
- LCOS (Stanford)
- LCPM (MGH)
- MISCAN-Lung (Erasmus)
- SimSmoke (Georgetown)
- Smoking-Lung Cancer (Georgetown)
- MULU (Mount Sinai)
- ENGAGE (MDACC)
- YLCM (Yale)
- OncoSim-Lung (CPAC-StatCan)
- LMO (FHCC) (Historical)
Lung Model Comparison Grid (PDF, 161 KB)
See all Comparison Grids & Profiles (Includes historical versions)